Meet the toolkit
✉️ Accept your GitHub invitation
Agenda
- Demo: A reproducible data analysis
- R and RStudio
- R Markdown
- Git and GitHub
- Recap
A reproducible data analysis
Let's talk about the Oscar nominations!

Recap: What did we just do?
- Locate a repository on GitHub
- Clone and open the project in RStudio
- Run the analysis using R Markdown
- Edit the analysis to exclude movie titles
- Re-run the analysis using R Markdown
Toolkit
- Scriptability → R
- Literate programming (code, narrative, output in one place) → R Markdown
- Version control → Git / GitHub
What is R/RStudio?
- R is a statistical programming language
- RStudio is a convenient interface for R (an integreated development environment, IDE)
- At its simplest:➥
- R is like a car’s engine
- RStudio is like a car’s dashboard
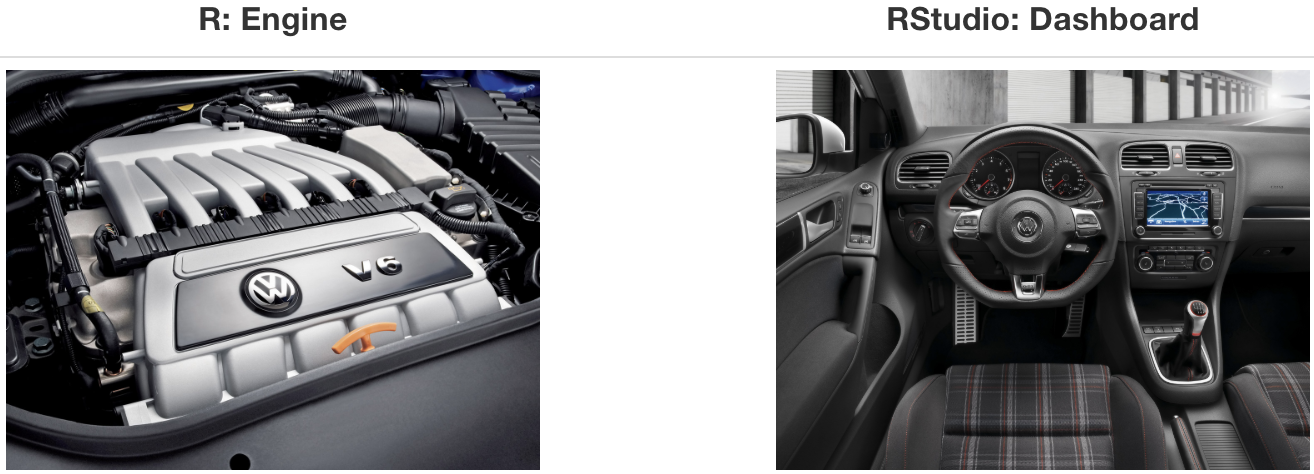

➥ Source: Modern Dive
Let's take a tour - R / RStudio

Concepts introduced:
- Console
- Using R as a calculator
- Environment
- Loading and viewing a data frame
- Accessing a variable in a data frame
- R functions
R essentials
A short list (for now):
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parantheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)R essentials
A short list (for now):
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parantheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)- Columns (variables) in data frames are accessed with
$:
dataframe$var_nameR essentials
A short list (for now):
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parantheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)- Columns (variables) in data frames are accessed with
$:
dataframe$var_name- Packages are installed with the
install.packagesfunction and loaded with thelibraryfunction, once per session:
install.packages("package_name")library(package_name)tidyverse
- The tidyverse is an opinionated collection of R packages designed for data analysis and data science.
- All packages share an underlying philosophy and a common grammar.
tidymodels

- tidymodels is an opinionated collection of R packages designed for modeling and statistical analysis.
- All packages share an underlying philosophy and a common grammar.
R Markdown
- Fully reproducible reports -- each time you knit the analysis is run from the beginning
- Simple markdown syntax for text
- Code goes in chunks, defined by three backticks, narrative goes outside of chunks
Let's take a tour - R Markdown

Concepts introduced:
- Knitting documents
- R Markdown and (some) R syntax
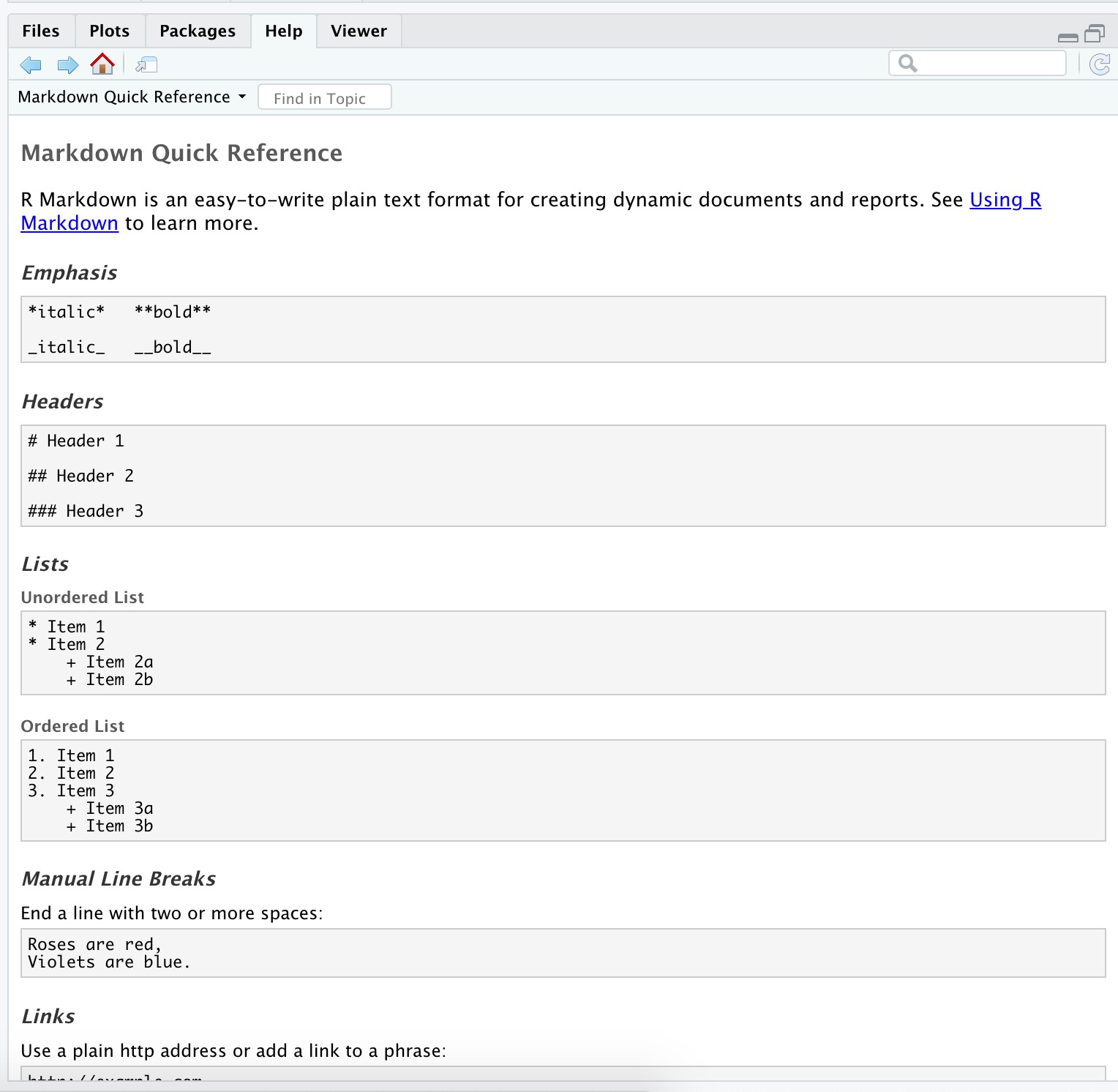
R Markdown help
Markdown Quick ReferenceHelp -> Markdown Quick Reference
Workspaces
Remember this, and expect it to bite you a few times as you're learning to work with R Markdown: The workspace of your R Markdown document is separate from the Console!
- If I run the following in the console
x <- 2x * 3Workspaces
Remember this, and expect it to bite you a few times as you're learning to work with R Markdown: The workspace of your R Markdown document is separate from the Console!
- If I run the following in the console
x <- 2x * 3All looks good, eh?
Workspaces
Remember this, and expect it to bite you a few times as you're learning to work with R Markdown: The workspace of your R Markdown document is separate from the Console!
- If I run the following in the console
x <- 2x * 3All looks good, eh?
- Then, if I add the following chunk in my R Markdown document
x * 3Workspaces
Remember this, and expect it to bite you a few times as you're learning to work with R Markdown: The workspace of your R Markdown document is separate from the Console!
- If I run the following in the console
x <- 2x * 3All looks good, eh?
- Then, if I add the following chunk in my R Markdown document
x * 3What happens? Why the error?
How will we use R Markdown?
- Every assignment / report / project / etc. is an R Markdown document
- You'll always have a template R Markdown document to start with
- The amount of scaffolding in the template will decrease over the semester
How do we collaborate?
- The statistical programming language we'll use is R
- The software we use to interface with R is RStudio
- But how do I get you the course materials that you can build on for your assignments?
- Hint: I'm not going to email you documents, that would be a mess!
Version control
- We introduced GitHub as a platform for collaboration
- But it's much more than that...
- It's actually desiged for version control
Versioning
with human readable messages
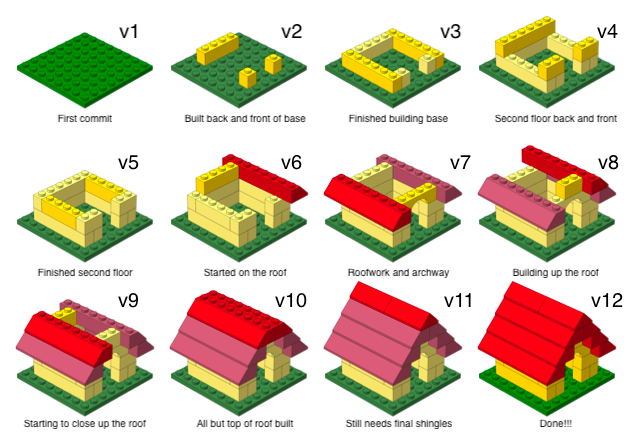
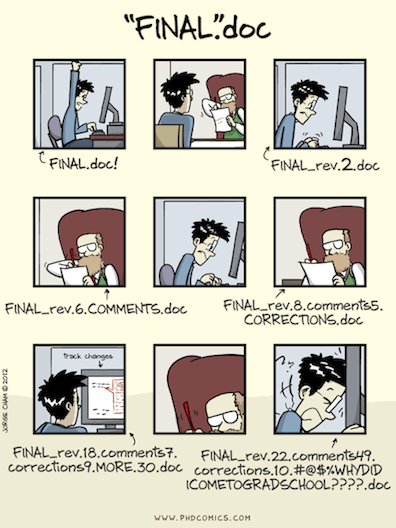
Why do we need version control?
Git and GitHub tips
- Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word on steroids. GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet -- like DropBox but much, much better).
Git and GitHub tips
- Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word on steroids. GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet -- like DropBox but much, much better).
- There are millions of git commands -- ok, that's an exaggeration, but there are a lot of them -- and very few people know them all. 99% of the time you will use git to add, commit, push, and pull.
Git and GitHub tips
- Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word on steroids. GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet -- like DropBox but much, much better).
- There are millions of git commands -- ok, that's an exaggeration, but there are a lot of them -- and very few people know them all. 99% of the time you will use git to add, commit, push, and pull.
- We will be doing Git things and interfacing with GitHub through RStudio, but if you google for help you might come accross methods for doing these things in the command line -- skip that and move on to the next resource unless you feel comfortable trying it out.
Git and GitHub tips
- Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word on steroids. GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet -- like DropBox but much, much better).
- There are millions of git commands -- ok, that's an exaggeration, but there are a lot of them -- and very few people know them all. 99% of the time you will use git to add, commit, push, and pull.
- We will be doing Git things and interfacing with GitHub through RStudio, but if you google for help you might come accross methods for doing these things in the command line -- skip that and move on to the next resource unless you feel comfortable trying it out.
- There is a great resource for working with git and R: happygitwithr.com. Some of the content in there is beyond the scope of this course, but it's a good place to look for help.
Let's take a tour -- Git / GitHub

Concepts introduced:
- Connect an R project to Github repository
- Working with a local and remote repository
- Committing, Pushing and Pulling
There is just a bit more of GitHub that we'll use in this class, but for today this is enough.
Recap
Can you answer these questions?
- What is reproducible data analysis, and why do we care?
- What is version control, and why do we care?
- What is R vs RStudio?
- What is git vs GitHub (and do I need to care)?