Logistic regression, LDA, QDA - Part 2
Dr. D’Agostino McGowan
LDA
- Go to the sta-363-s20 GitHub organization and search for
appex-02-lda - Clone this repository into RStudio Cloud
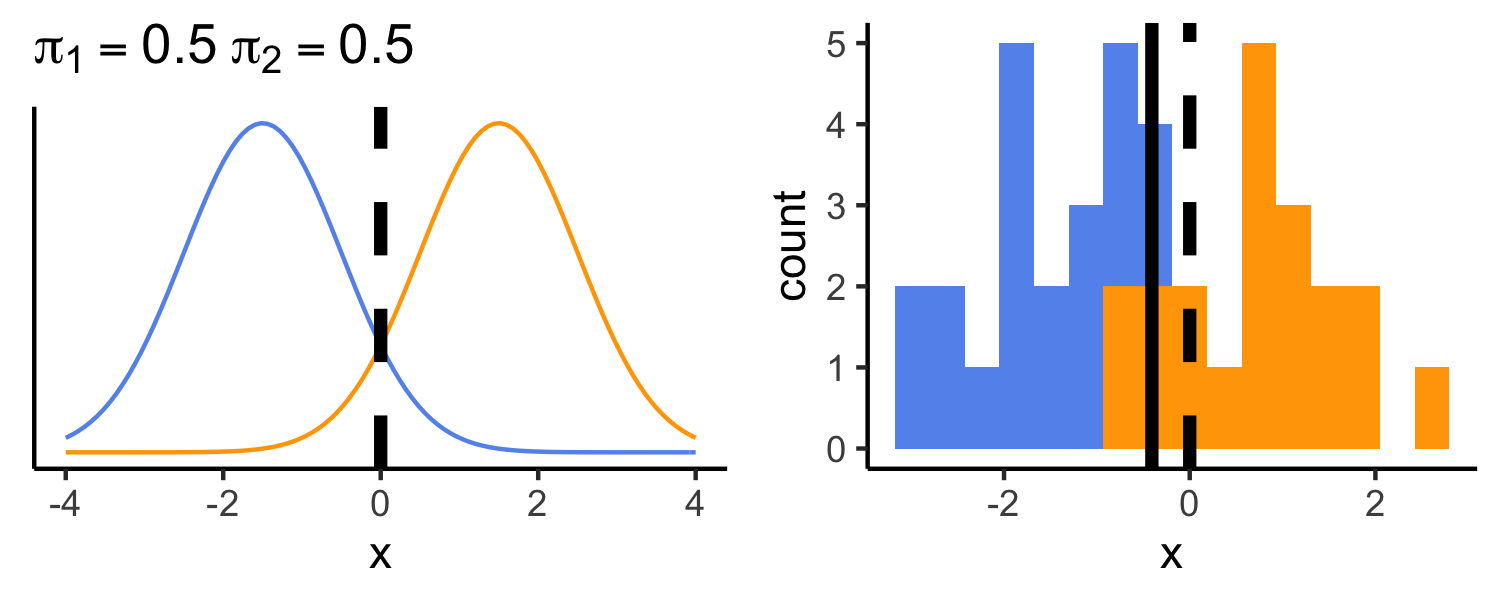
- μ1=−1.5
- μ2=1.5
- π1=π2=0.5
- σ2=1

- μ1=−1.5
- μ2=1.5
- π1=π2=0.5
- σ2=1
- typically we don't know the true parameters, we just use our training data to estimate them
Estimating parameters
^πk=nkn
Estimating parameters
^πk=nkn ^μk=1nk∑i:yi=kxi
Estimating parameters
^πk=nkn ^μk=1nk∑i:yi=kxi
^σ2=1n−KK∑k=1∑i:yi=k(xi−^μk)2=K∑k=1nk−1n−K^σ2k
Estimating parameters
^πk=nkn ^μk=1nk∑i:yi=kxi
^σ2=1n−KK∑k=1∑i:yi=k(xi−^μk)2=K∑k=1nk−1n−K^σ2k
^σ2k=1nk−1∑i:yi=k(xi−^μk)2
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n))## # A tibble: 3 x 3## y n pi## <dbl> <int> <dbl>## 1 1 5 0.333## 2 2 5 0.333## 3 3 5 0.333Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n))## # A tibble: 3 x 3## y n pi## <dbl> <int> <dbl>## 1 1 5 0.333## 2 2 5 0.333## 3 3 5 0.333group_by(): do calculations on groups
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n))## # A tibble: 3 x 3## y n pi## <dbl> <int> <dbl>## 1 1 5 0.333## 2 2 5 0.333## 3 3 5 0.333group_by(): do calculations on groupssummarise(): reduce variables to values
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n))## # A tibble: 3 x 3## y n pi## <dbl> <int> <dbl>## 1 1 5 0.333## 2 2 5 0.333## 3 3 5 0.333group_by(): do calculations on groupssummarise(): reduce variables to valuesmutate(): add new variables
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n))group_by(): do calculations on groupssummarise(): reduce variables to valuesmutate(): add new variables
How do we pull πk out into their own R object?
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(n = n()) %>% mutate(pi = n / sum(n)) %>% pull(pi) -> piHow do we pull πk out into their own R object?
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^πk=nkn
pi## [1] 0.3333333 0.3333333 0.3333333How do we pull πk out into their own R object?
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^μk=1nk∑i:yi=kxi
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(mu = mean(x))## # A tibble: 3 x 2## y mu## <dbl> <dbl>## 1 1 -1.46## 2 2 1.5 ## 3 3 3.54Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^μk=1nk∑i:yi=kxi
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(mu = mean(x)) %>% pull(mu) -> muEstimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^σ2=K∑k=1nk−1n−K^σ2k
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(var_k = var(x), n = n()) %>% mutate(v = ((n - 1) / (sum(n) - 3)) * var_k) %>% summarise(sigma_sq = sum(v))## # A tibble: 1 x 1## sigma_sq## <dbl>## 1 1.47Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^σ2=K∑k=1nk−1n−K^σ2k
df %>% group_by(y) %>% summarise(var_k = var(x), n = n()) %>% mutate(v = ((n - 1) / (sum(n) - 3)) * var_k) %>% summarise(sigma_sq = sum(v)) %>% pull(sigma_sq) -> sigma_sqEstimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
δk(x)=xμkσ2−μ2k2σ2+log(πk)
- Let's predict the class for x=2
x <- 2x * (mu / sigma_sq) - mu^2 / (2 * sigma_sq) + log(pi)## [1] -3.8155857 0.1795063 -0.5436021Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
δk(x)=xμkσ2−μ2k2σ2+log(πk)
- Let's predict the class for x=2
x <- 2x * (mu / sigma_sq) - mu^2 / (2 * sigma_sq) + log(pi)## [1] -3.8155857 0.1795063 -0.5436021Which class should we give this point?
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
δk(x)=xμkσ2−μ2k2σ2+log(πk)
- Let's predict the class for x=6
x <- 6x * (mu / sigma_sq) - mu^2 / (2 * sigma_sq) + log(pi)## [1] -7.796499 4.269486 9.108750Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
δk(x)=xμkσ2−μ2k2σ2+log(πk)
- Let's predict the class for x=6
x <- 6x * (mu / sigma_sq) - mu^2 / (2 * sigma_sq) + log(pi)## [1] -7.796499 4.269486 9.108750Which class should we give this point?
From the discriminant score to probabilities
We can turn ^δk(x) into estimates for class probabilities
From the discriminant score to probabilities
We can turn ^δk(x) into estimates for class probabilities
^P(Y=k|X=x)=e^δk(x)∑Kl=1e^δl(x)
From the discriminant score to probabilities
We can turn ^δk(x) into estimates for class probabilities
^P(Y=k|X=x)=e^δk(x)∑Kl=1e^δl(x)
- Classifying the largest ^δk(x) is the same as classifying to the class with the largest ^P(Y=k|X=x)
From the discriminant score to probabilities
We can turn ^δk(x) into estimates for class probabilities
^P(Y=k|X=x)=e^δk(x)∑Kl=1e^δl(x)
- Classifying the largest ^δk(x) is the same as classifying to the class with the largest ^P(Y=k|X=x)
- For K=2:
- classify to 2 if ^P(Y=2|X=x)≥0.5
- classify to 1 otherwise
Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
^P(Y=k|X=x)=e^δk(x)∑Kl=1e^δl(x)
- Let's get the posterior probability of each class for x=6
x <- 6d <- x * (mu / sigma_sq) - mu^2 / (2 * sigma_sq) + log(pi)exp(d) / sum(exp(d))## [1] 4.515655e-08 7.850755e-03 9.921492e-01Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
- There is a function to do this in R called
lda()in the MASS package
library(MASS)model <- lda(y ~ x, data = df)Estimating parameters (in R!)
| x | -1.6 | 0.2 | -0.9 | -2.0 | -3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
- There is a function to do this in R called
lda()in the MASS package
library(MASS) model <- lda(y ~ x, data = df)predict(model, newdata = data.frame(x = 6))## $class## [1] 3## Levels: 1 2 3## ## $posterior## 1 2 3## 1 4.515655e-08 0.007850755 0.9921492## ## $x## LD1## 1 3.968523 LDA
- Go to the sta-363-s20 GitHub organization and search for
appex-02-lda - Clone this repository into RStudio Cloud
- Complete the exercises
- Knit, Commit, Push
Linear discriminant analysis p>1
- When p>1 the density takes on the multivariate normal density
f(x)=1(2π)p/2|Σ|1/2e−12(x−μ)TΣ−1(x−μ)
Linear discriminant analysis p>1

- The discriminant function is now
δk(x)=xTΣ−1μk−12μTkΣ−1μk+logπk
- This is still a linear function!
Example p=2, K=3
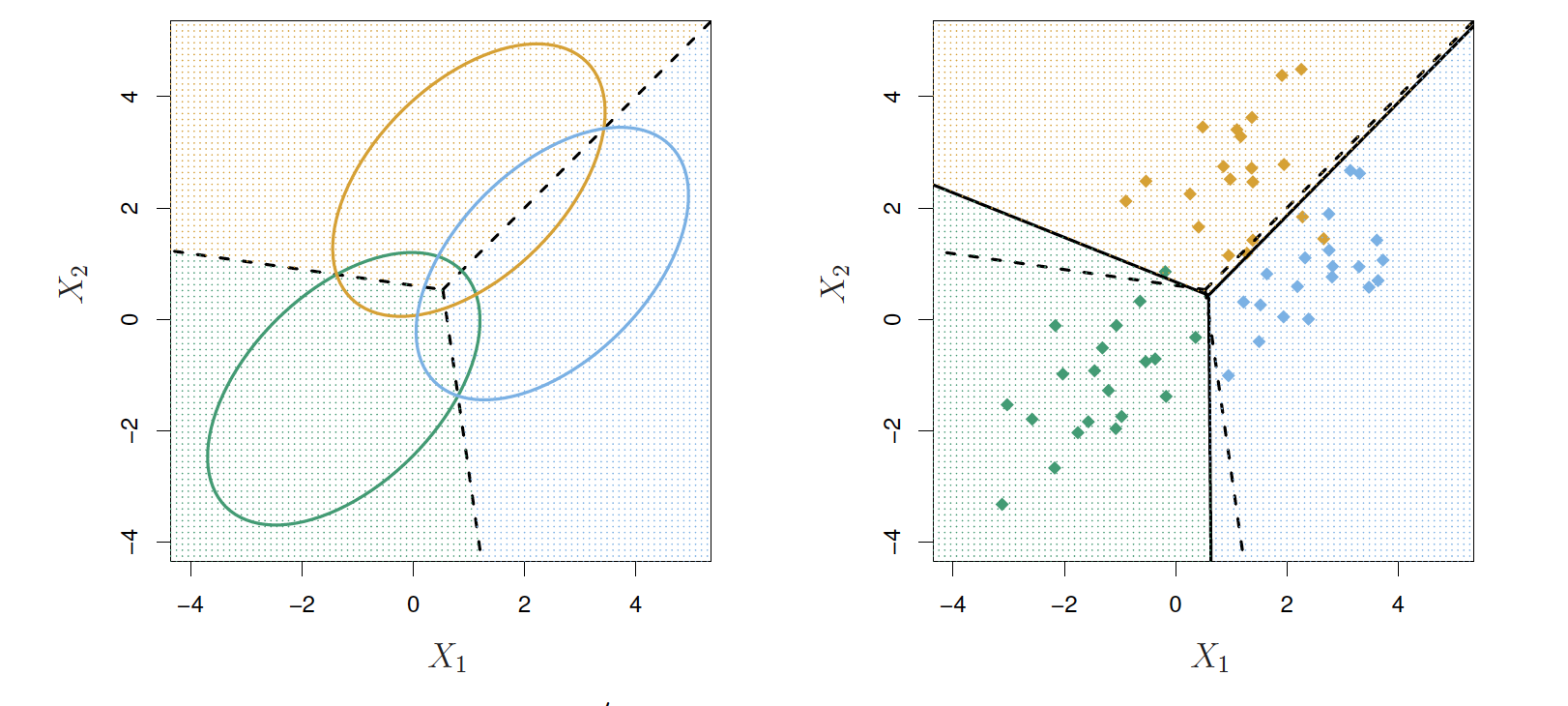
- Here π1=π2=π3=1/3
- The dashed lines the Bayes decision boundaries
- If they were known, they would yield the fewest misclassification errors, among all possible classifiers.
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
What is the misclassification rate?
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
What is the misclassification rate?
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
What is the misclassification rate?
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
Since this is training error what is a possible concern?
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
What is the misclassification rate?
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
Since this is training error what is a possible concern?
- This could be overfit
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
This could be overfit- Since we have a large n and small p ( n=10,000, p=4 ) we aren't too worried about overfitting
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
What would the error rate be if we classified to the prior,
Nodefault?
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
What would the error rate be if we classified to the prior,
Nodefault? - 333/10000 - 3.33%
LDA on Credit Data
| True Default (No) | True Default (Yes) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Default (No) | 9644 | 252 | 9895 |
| Predicted Default (Yes) | 23 | 81 | 104 |
| Total | 9667 | 333 | 10000 |
- 23+25210000 errors - 2.75% misclassification
- Since we have a large n and small p ( n=10,000, p=4 ) we aren't too worried about overfitting
- Of the true
No's, we make 23/9667=0.2% errors; of the trueYes's, we make 252/333=75.7% errors!
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
What is the false positive rate in the Credit Default example?
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
What is the false positive rate in the Credit Default example?
- 0.2%
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
What is the false positive rate in the Credit Default example?
What is the false negative rate in the Credit Default example?
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
What is the false positive rate in the Credit Default example?
- 0.2%
What is the false negative rate in the Credit Default example?
- 75.7%
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
- The Credit Default table was created by predicting the
Yesclass if
^P(Default|Balance, Student)≥0.5
Types of errors
- False positive rate: The fraction of truly negative that are classified as positive
- False negative rate: The fraction of truly positive that are classified as negative
- The Credit Default table was created by predicting the
Yesclass if
^P(Default|Balance, Student)≥0.5 We can change the two error rates by changing the *threshold from 0.5 to some other number between 0 and 1
^P(Default|Balance, Student)≥threshold
Varying the threshold
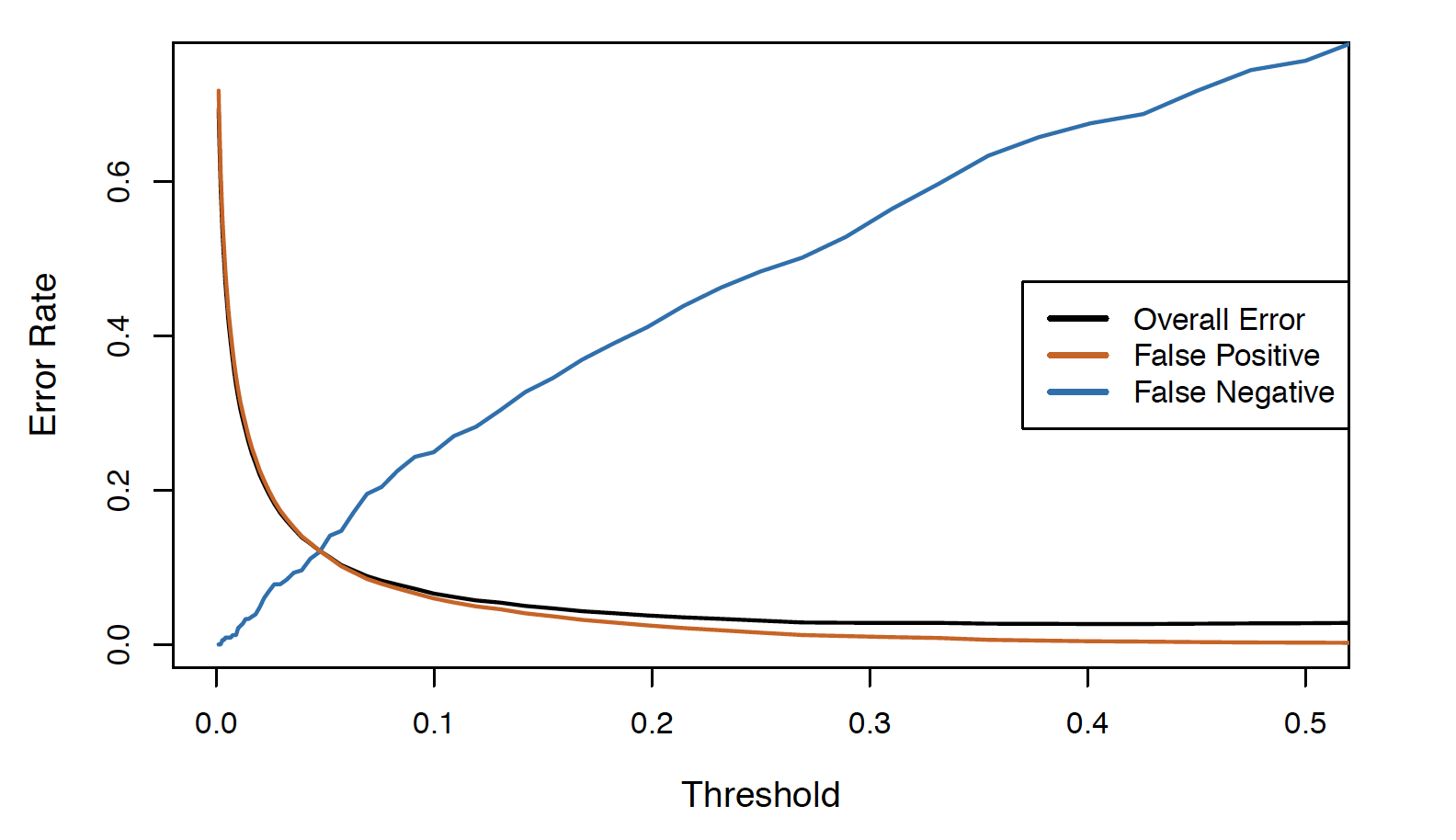
- To reduce the false negative rate we may want the threshold to be 0.1 or less
ROC
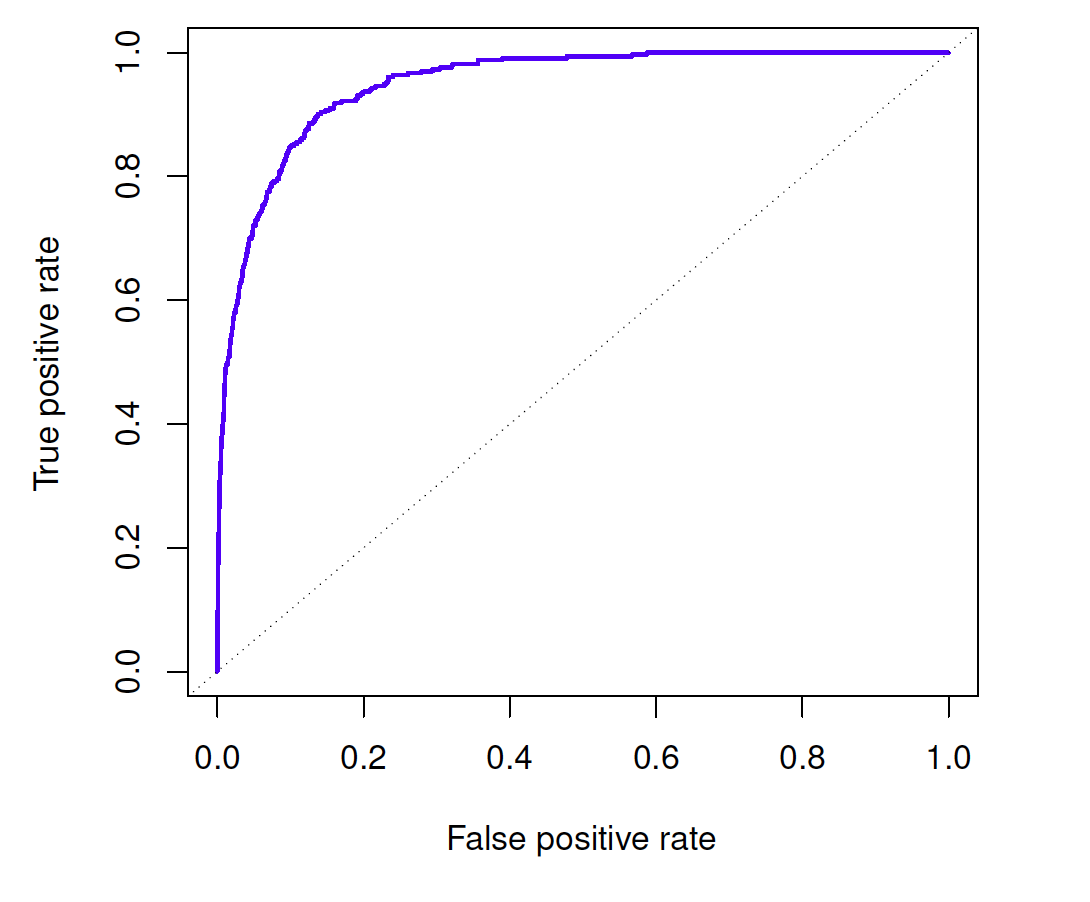
- A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve looks at both simultaneously
- The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is sometimes a metric for performance
ROC

- A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve looks at both simultaneously
- The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is sometimes a metric for performance
Which do you think is better, higher or lower AUC?
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)- Use the
lda()function in R from the MASS package
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)- Use the
lda()function in R from theMASSpackage - Get the predicted classes along with posterior probabilities using the
predict()function
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)Default %>% mutate(predicted_class = predictions$class)- Use the
lda()function in R from theMASSpackage - Get the predicted classes along with posterior probabilities using the
predict()function - Add the predicted class using the
mutate()function
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)Default %>% mutate(predicted_class = predictions$class) %>% summarise(fpr = sum(default == "No" & predicted_class == "Yes") / sum(default == "No"), fnr = sum(default == "Yes" & predicted_class == "No") / sum(default == "Yes"))## fpr fnr## 1 0.002275784 0.7627628- Use the
summarise()function to add the false positive and false negative rates
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)library(tidymodels)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)Default %>% mutate(predicted_class = predictions$class) %>% conf_mat(default, predicted_class) %>% autoplot(type = "heatmap")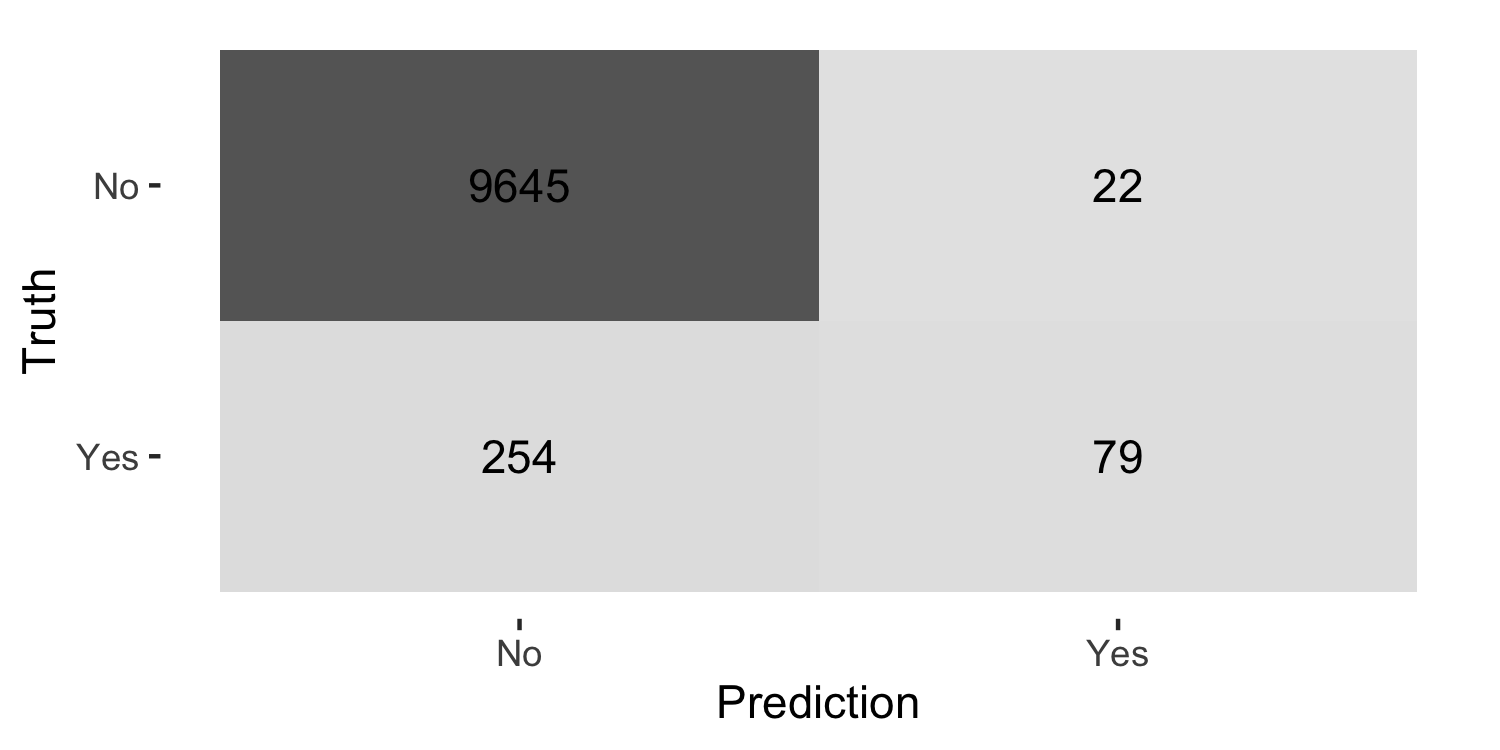
Let's see it in R
conf_mat()expects your outcome to be a factor variable
library(MASS)library(tidymodels)model <- lda(default ~ balance + student + income, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)Default %>% mutate(predicted_class = predictions$class, default = as.factor(default)) %>% conf_mat(default, predicted_class) %>% autoplot(type = "heatmap")