Logistic regression, LDA, QDA - Part 3
Dr. D’Agostino McGowan
Other forms of discriminant analysis
P(Y|X)=πkfk(x)∑Kl=1πlfl(x)
Other forms of discriminant analysis
P(Y|X)=πkfk(x)∑Kl=1πlfl(x)
- When fk(x) are normal densities with the same covariance matrix Σ in each class, this is linear discriminant analysis
Other forms of discriminant analysis
P(Y|X)=πkfk(x)∑Kl=1πlfl(x)
- When fk(x) are normal densities with the same covariance matrix Σ in each class, this is linear discriminant analysis
- When fk(x) are normal densities with different covariance matrices Σk in each class, this is quadratic discriminant analysis
Other forms of discriminant analysis
P(Y|X)=πkfk(x)∑Kl=1πlfl(x)
- When fk(x) are normal densities with the same covariance matrix Σ in each class, this is linear discriminant analysis
- When fk(x) are normal densities with different covariance matrices Σk in each class, this is quadratic discriminant analysis
- Lots of other forms are possible!
Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
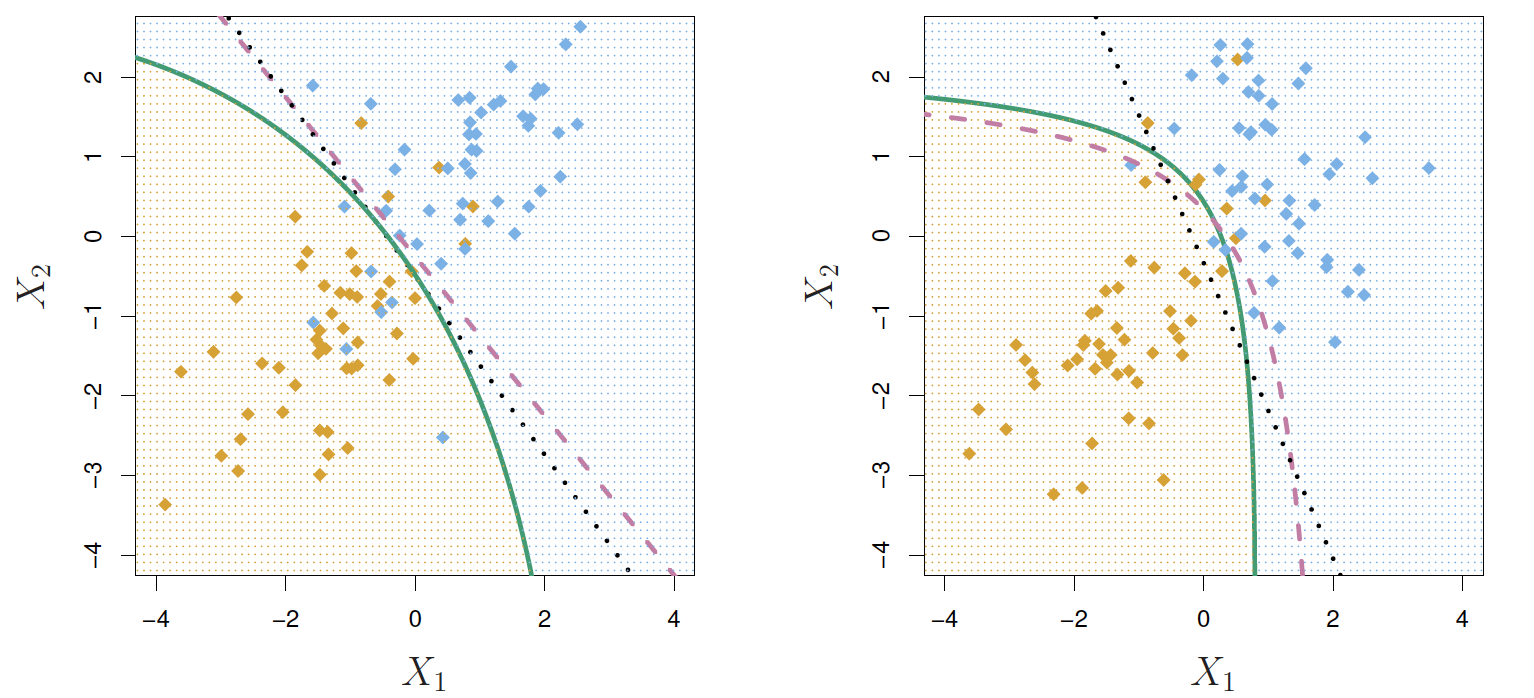
δk(x)=−12(x−μk)TΣ−1k(x−μk)+logπk
Why do you think this is called quadratic discriminant analysis?
Quadratic Discriminant Analysis

δk(x)=−12(x−μk)TΣ−1k(x−μk)+logπk
Why do you think this is called quadratic discriminant analysis?
- Because the Σk are different, the quadratic terms matter
Let's see it in R
library(MASS)model <- qda(default ~ balance + student, data = Default)predictions <- predict(model)- Use the
qda()function in R from the MASS package
Let's see it in R
- Let's use LDA to visualize the data
model <- lda(Species ~ ., data = iris)predictions <- predict(model)Let's see it in R
- Let's use LDA to visualize the data
model <- lda(Species ~ ., data = iris) predictions <- predict(model)plot_data <- data.frame(outcome = iris$Species, lda = predictions$x)head(plot_data)## outcome lda.LD1 lda.LD2## 1 setosa 8.061800 0.3004206## 2 setosa 7.128688 -0.7866604## 3 setosa 7.489828 -0.2653845## 4 setosa 6.813201 -0.6706311## 5 setosa 8.132309 0.5144625## 6 setosa 7.701947 1.4617210Let's see it in R
- Let's use LDA to visualize the data
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point()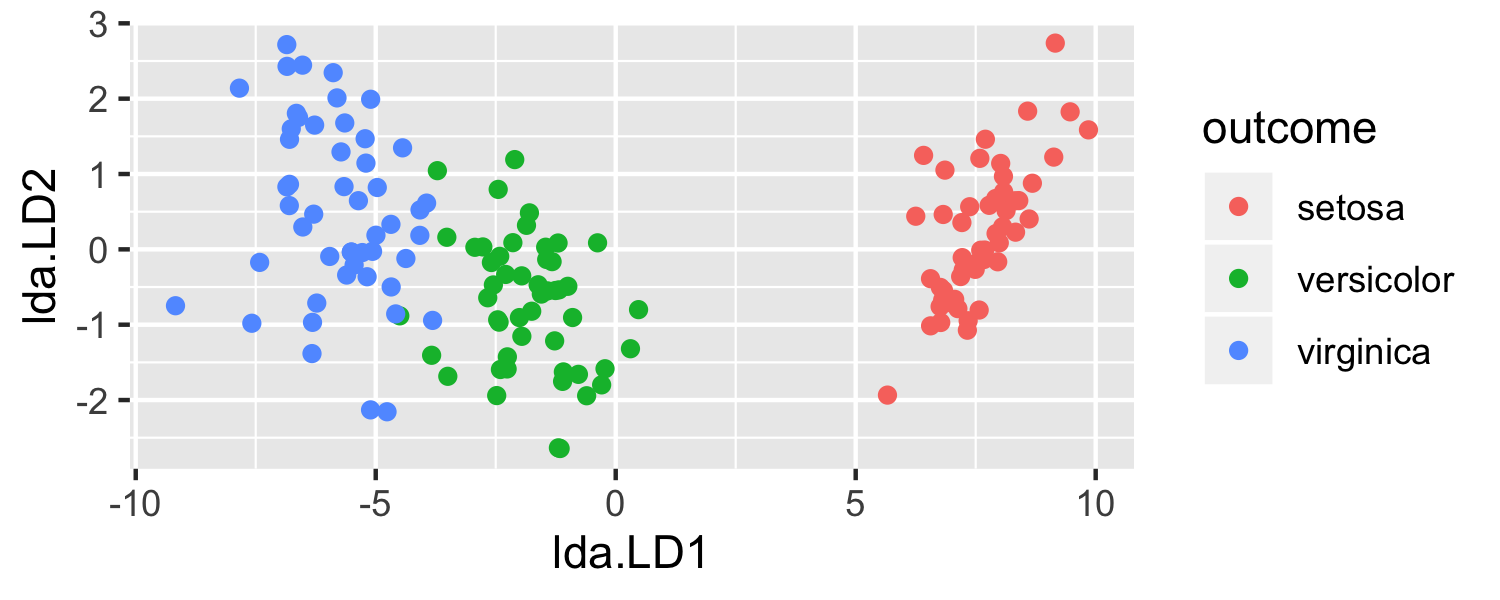
ggplot2 ∈ tidyverse

- ggplot2 is tidyverse's data visualization package
- The
ggin "ggplot2" stands for Grammar of Graphics - It is inspired by the book Grammar of Graphics by Leland Wilkinson †
- A grammar of graphics is a tool that enables us to concisely describe the components of a graphic

† Source: BloggoType
ggplot2
What function creates the plot?
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point() + labs(x = "LD1", y = "LD2")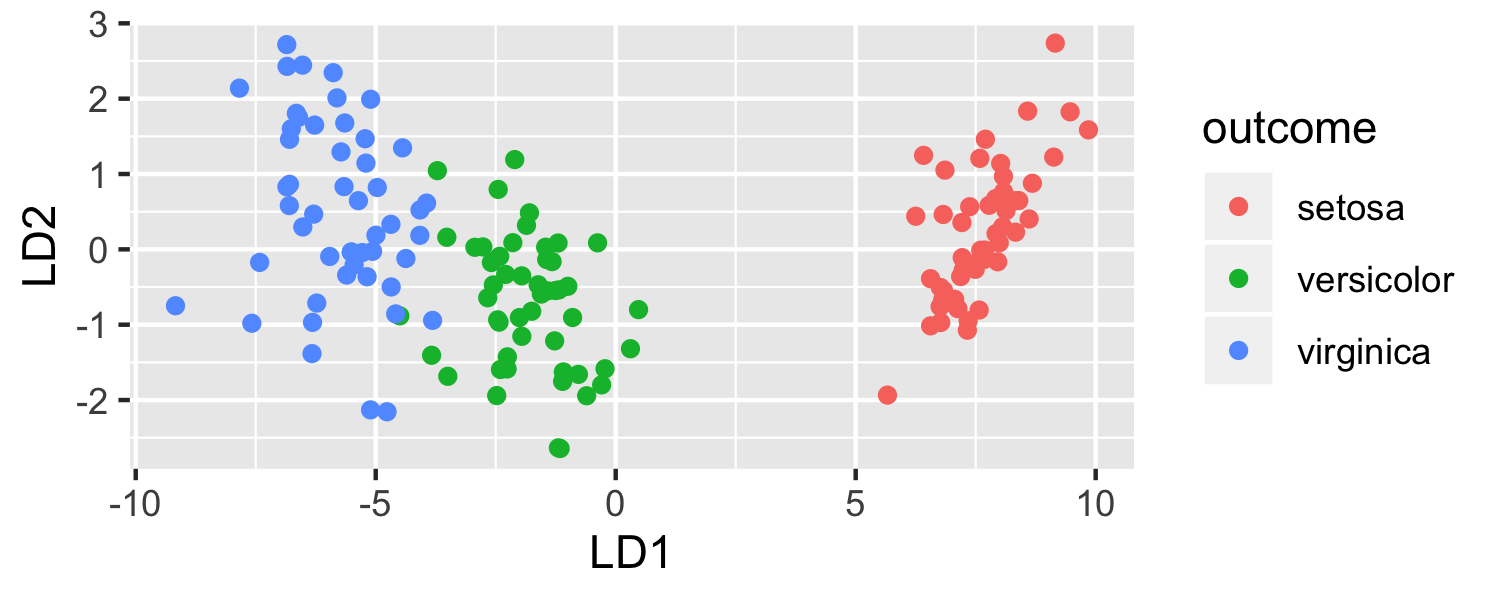
ggplot2
What data set is being plotted?
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point() + labs(x = "LD1", y = "LD2")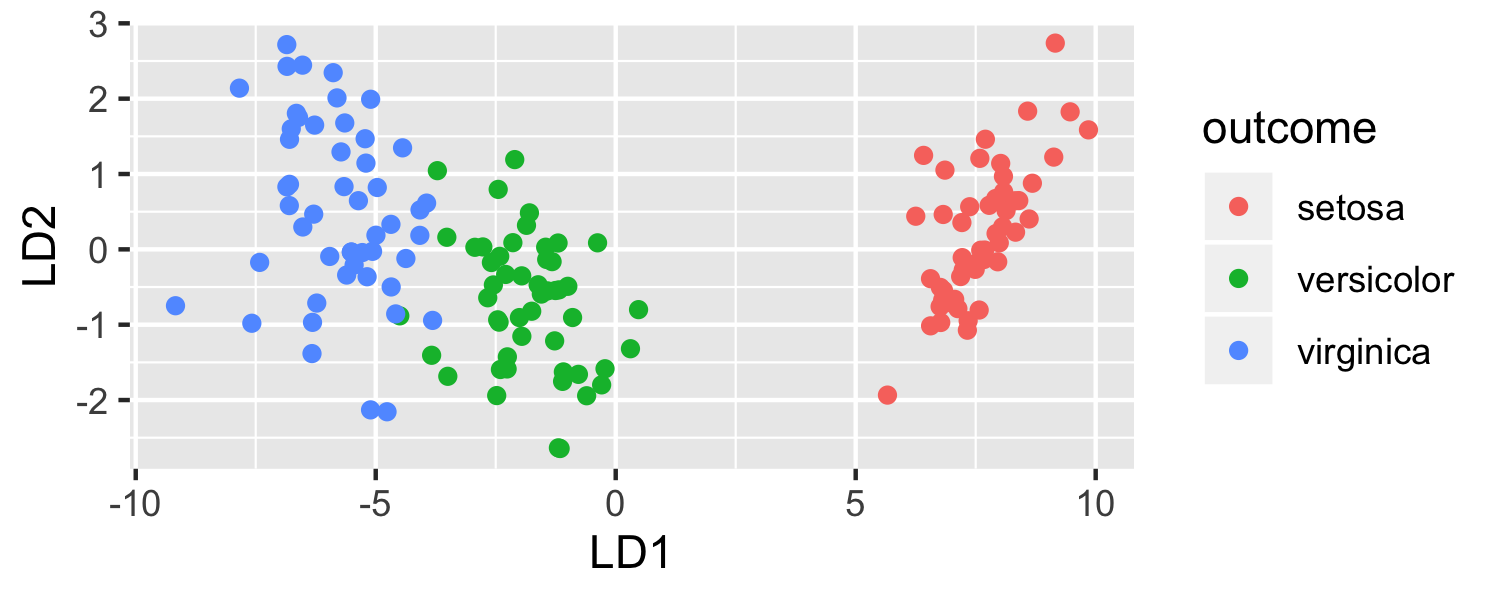
ggplot2
Which variables are on the x- and y-axis?
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point() + labs(x = "LD1", y = "LD2")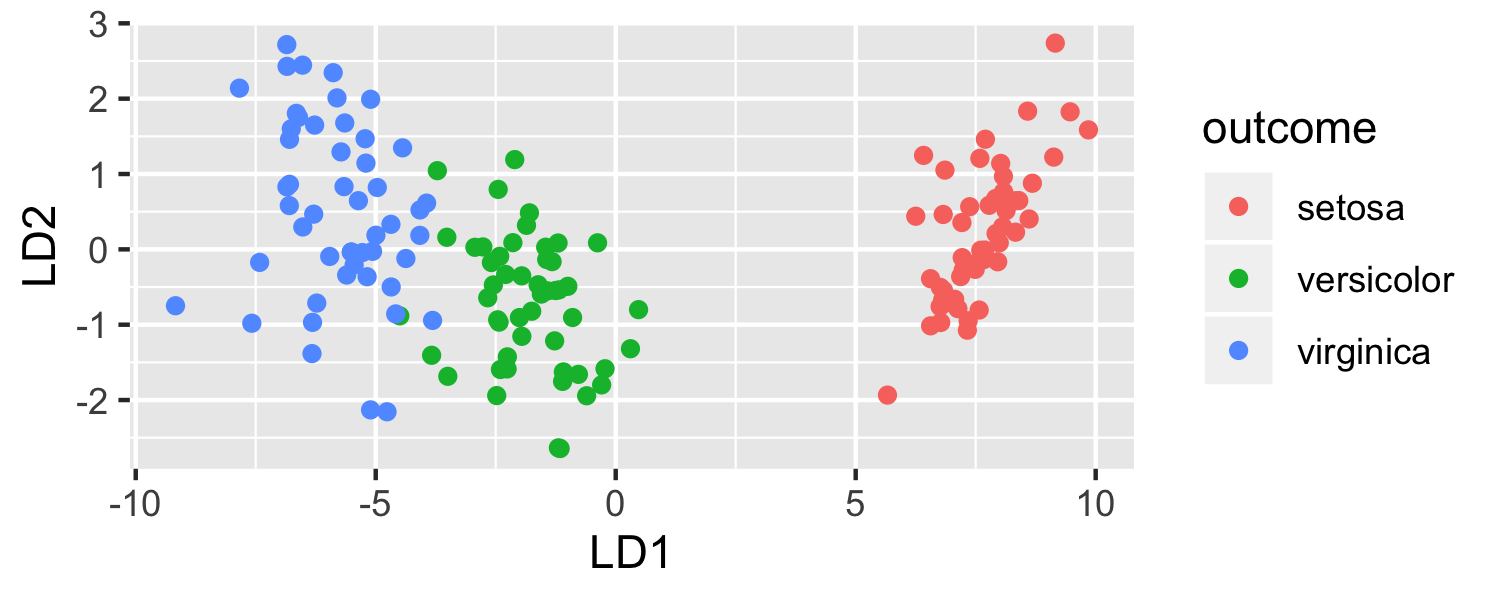
ggplot2
What variable in the dataset determines the color?
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point() + labs(x = "LD1", y = "LD2")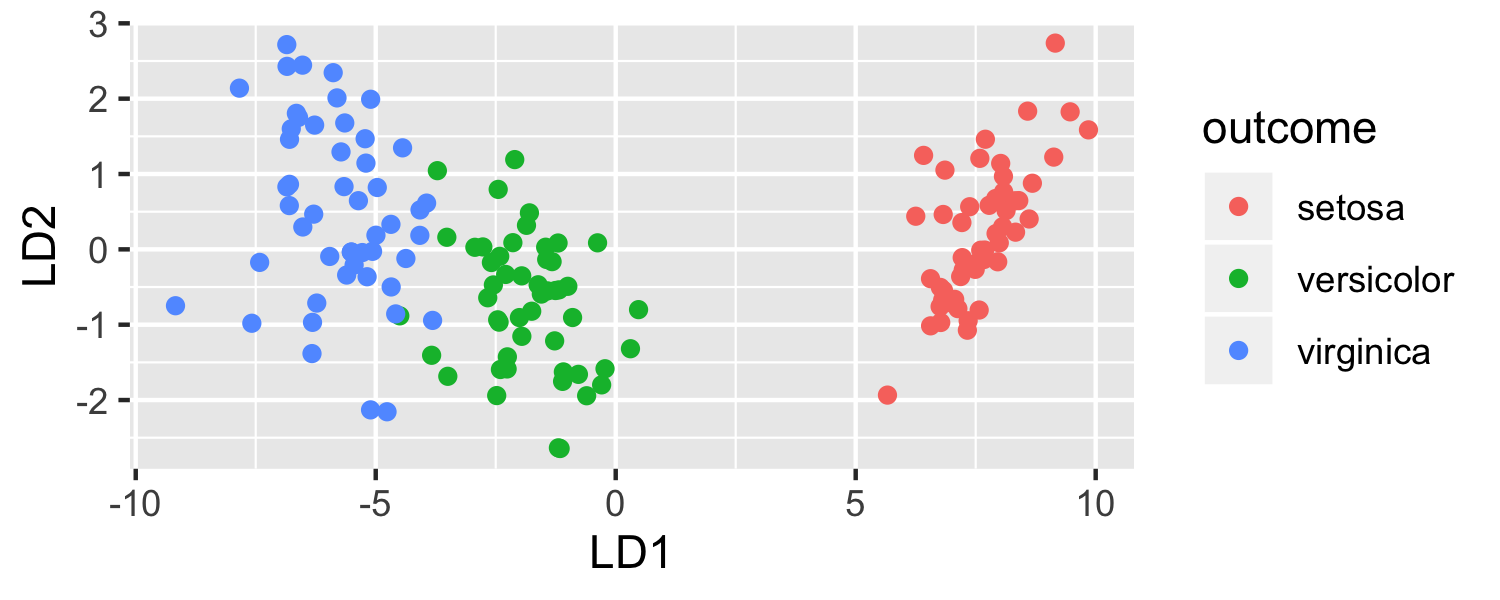
ggplot2
What does geom_point() mean?
ggplot(data = plot_data, mapping = aes(x = lda.LD1, y = lda.LD2, color = outcome)) + geom_point() + labs(x = "LD1", y = "LD2")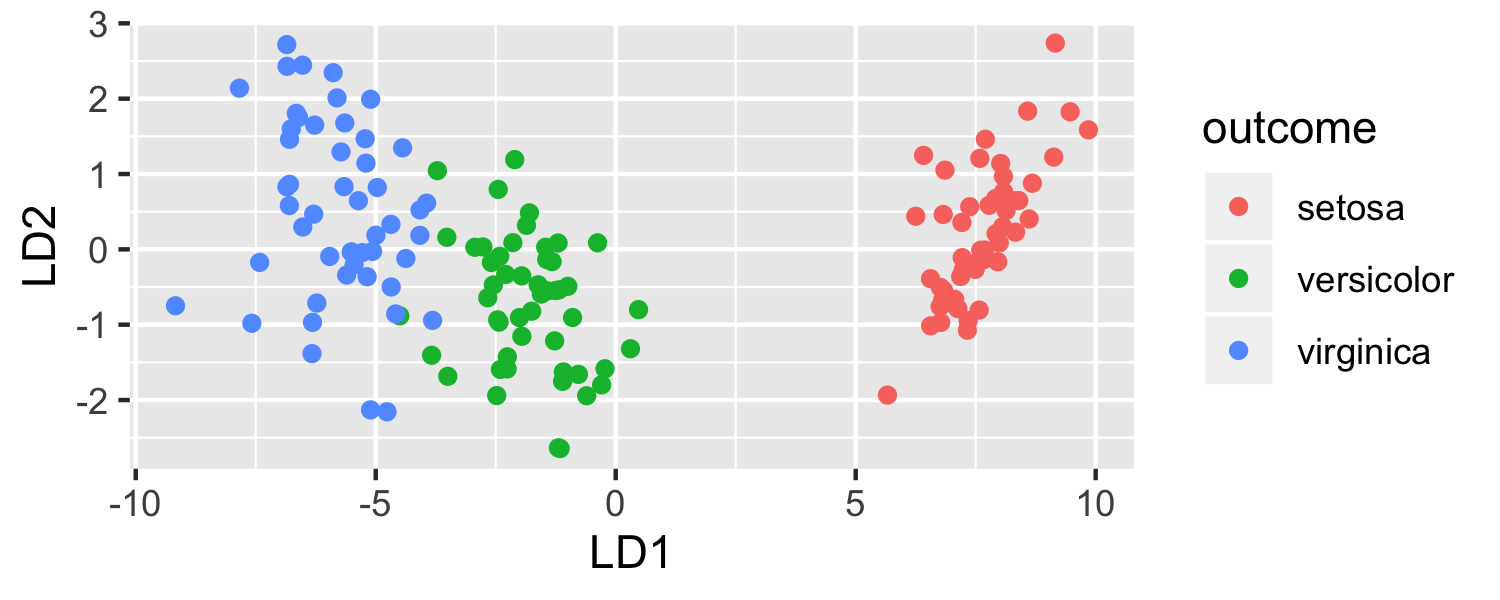
Hello ggplot2!
ggplot()is the main function in ggplot2 and plots are constructed in layers- The structure of the code for plots can often be summarized as
ggplot + geom_xxxHello ggplot2!
ggplot()is the main function in ggplot2 and plots are constructed in layers- The structure of the code for plots can often be summarized as
ggplot + geom_xxxor, more precisely
ggplot(data = [dataset], mapping = aes(x = [x-variable], y = [y-variable])) + geom_xxx() + other optionsHello ggplot2!
- To use ggplot2 functions, first load tidyverse
Hello ggplot2!
- To use ggplot2 functions, first load tidyverse
- For help with the ggplot2, see ggplot2.tidyverse.org
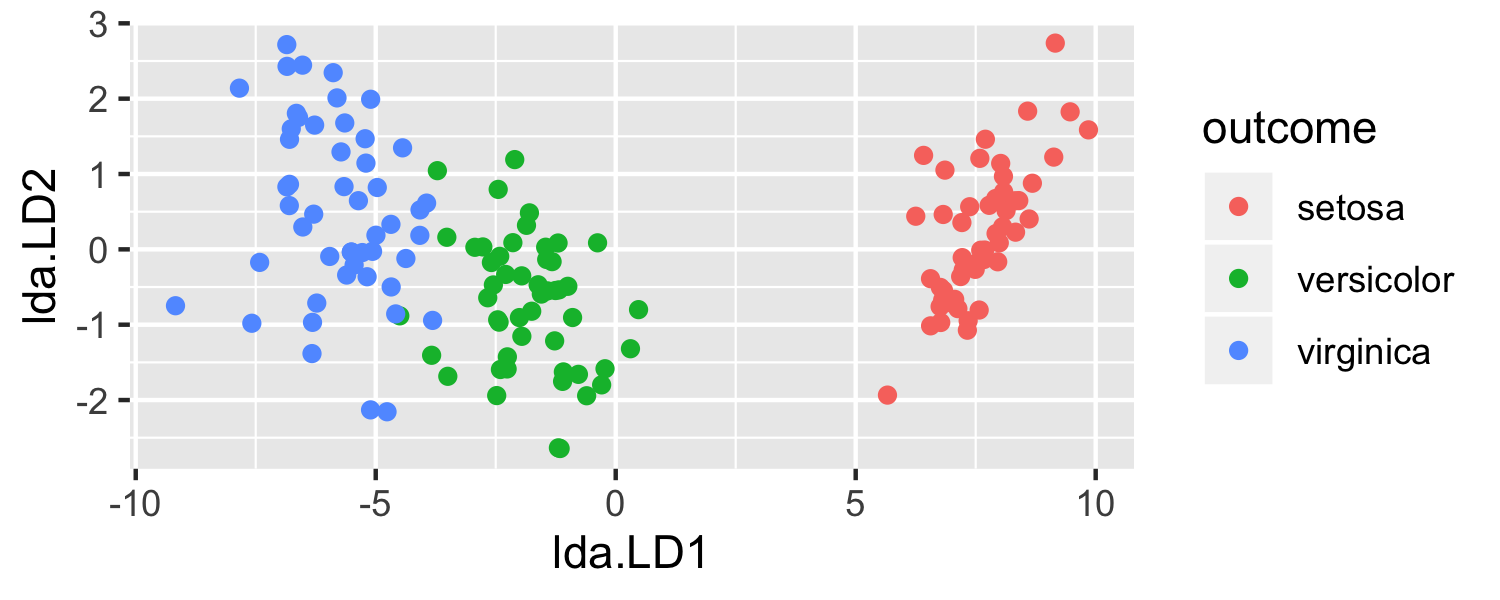
- What is going on here?

- What is going on here?
- LDA is projecting the samples X onto a hyperplane with K−1 dimensions.

- What is going on here?
- LDA is projecting the samples X onto a hyperplane with K−1 dimensions.
What is K here?
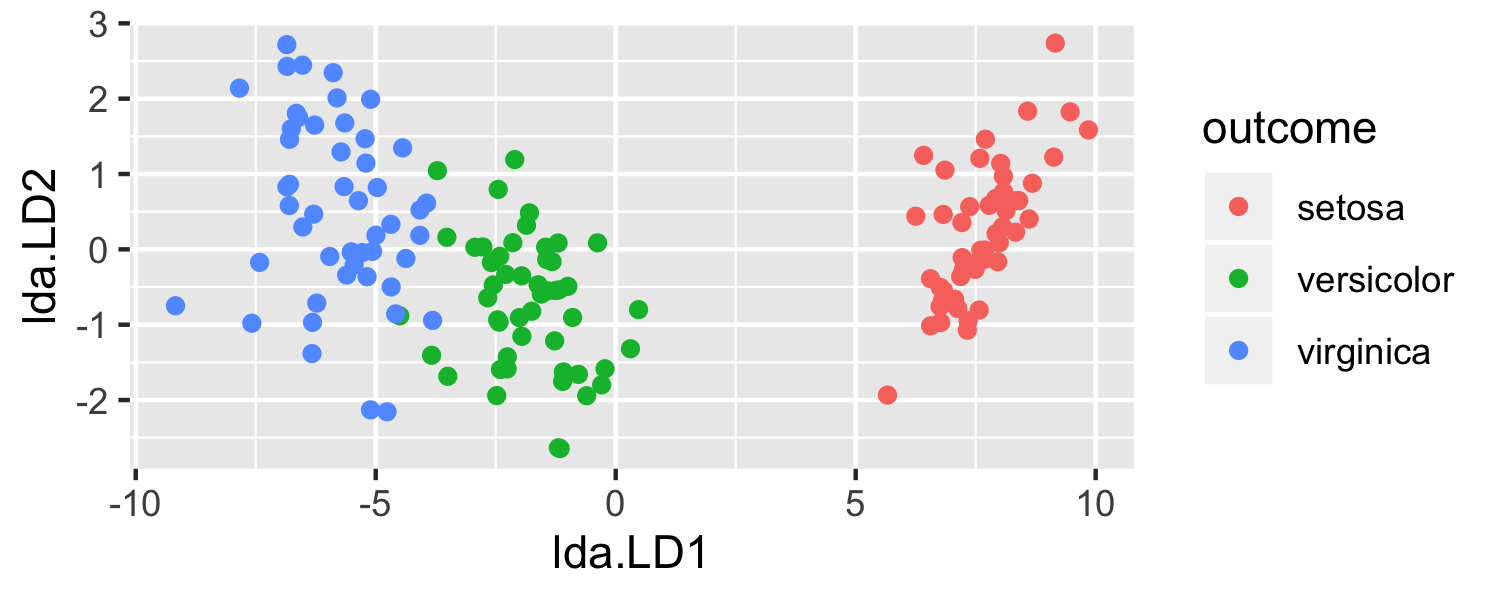
- What is going on here?
- LDA is projecting the samples X onto a hyperplane with K−1 dimensions.
- Why does this work?
- LDA essentially classifies to the closest centroid, and they span a K - 1 dimensional plane.

- What is going on here?
- LDA is projecting the samples X onto a hyperplane with K−1 dimensions.
- Why does this work?
- LDA essentially classifies to the closest centroid, and they span a K - 1 dimensional plane.
- Even when K > 3, we can find the "best" 2-dimensional plane for vizualizing the discriminant rule by using the first two discriminant variables (LD1 and LD2)
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
- This is the same form as logistic regression
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
- This is the same form as logistic regression
- The difference is in how the parameters are estimated
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
- This is the same form as logistic regression
- The difference is in how the parameters are estimated
- Logistic regression uses the conditional likelihood based on P(Y|X) (discriminative learning)
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
- This is the same form as logistic regression
- The difference is in how the parameters are estimated
- Logistic regression uses the conditional likelihood based on P(Y|X) (discriminative learning)
- LDA uses the full likelihood based on P(X,Y) (generative learning)
Logistic Regression versus LDA
- For the two-class problem ( K=2 ), LDA takes the form
log(p1(x)1−p1(x))=log(p1p2)=c0+c1x1+⋯+cpxp
- This is the same form as logistic regression
- The difference is in how the parameters are estimated
- Logistic regression uses the conditional likelihood based on P(Y|X) (discriminative learning)
- LDA uses the full likelihood based on P(X,Y) (generative learning)
- The results are often similar
Summary
- Logistic regression is very popular for classification, especially when K=2
- LDA is useful when n is small, or the classes are well separated, and normality assumptions are reasonable. Also when K>2
Summary
- Logistic regression is very popular for classification, especially when K=2
- LDA is useful when n is small, or the classes are well separated, and normality assumptions are reasonable. Also when K>2
- QDA is similar to LDA, but it is more flexible because it allows the covariance of the predictors to be different for each class, k
Summary
- Logistic regression is very popular for classification, especially when K=2
- LDA is useful when n is small, or the classes are well separated, and normality assumptions are reasonable. Also when K>2
- QDA is similar to LDA, but it is more flexible because it allows the covariance of the predictors to be different for each class, k
- See Section 4.5 in your book for some comparisons of logistic regression, LDA, and KNN.